
2020年这不堪回首的一年已只剩下了最后一天。对此,美银美林首席投资策略师Michael Hartnett用12张图表,回顾和总结了这一年全球市场的发展走向和运行轨迹。
首先,2020年毫无疑问是由新冠疫情主导的一年。正如美银所指出的,这一致命的病毒“蔓延成一场大流行病,粉碎了之前所有对2020年社会、政治、经济和金融市场走向的预测。”
截至年底,全球已有超过7500万人感染了新冠病毒,超过170万人死亡(图1),美国和欧洲受到的打击比亚洲更严重。
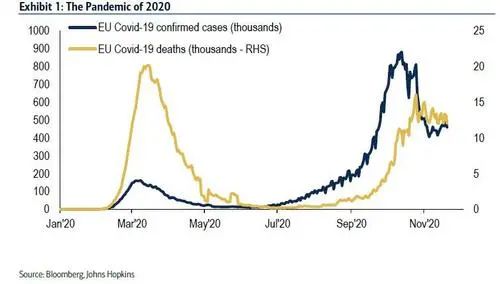
3月至5月的第一波疫情高峰引发了金融市场崩溃、封锁和衰退;致命程度较低的第二波秋季则并未再引发大规模的恐慌。
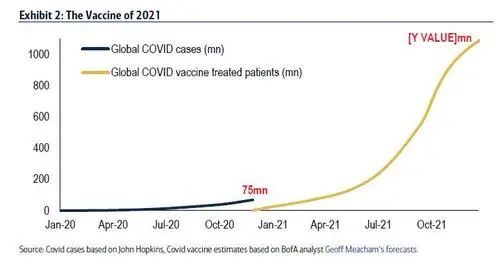
为应对疫情大流行,到2020年底,有多种新冠疫苗正在研发中,其中几款疫苗已经以前所未有的速度获批分发。
美国银行预测,到2021年年底,将有11亿人接种疫苗,这一数字将远远超过2020年迄今感染病毒的7500万人(图2)。
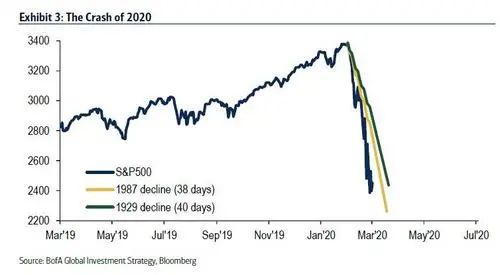
世界卫生组织于2020年3月10日首度将新冠病毒定义为全球大流行病。而由于市场预期,全球信贷和股票价格在2月和3月初便已大幅下跌……随后更是直线跳水。
在不到一个月的时间里,全球股市市值蒸发了30万亿美元(图3),无论是速度还是规模都堪称有史以来最大的崩盘之一。
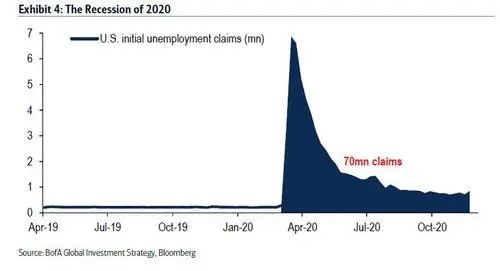
在第二季度,全球GDP蒸发了10万亿美元,随着人类“流动”的停止(美国运输安全管理局4月份航空旅客同比下降96%),油价更是一度变为负值。
2020年,一度有7000万美国人申请失业救济,失业率飙升至15%(图4);美国家庭储蓄率跃升至34%,创历史新高。
值得一提的是,在今年年初,投资者曾经对市场抱着非常乐观的心态。根据美国银行的牛熊指标(图5),市场情绪在3月中旬达到最大看跌水平,并一直保持到6月中旬。
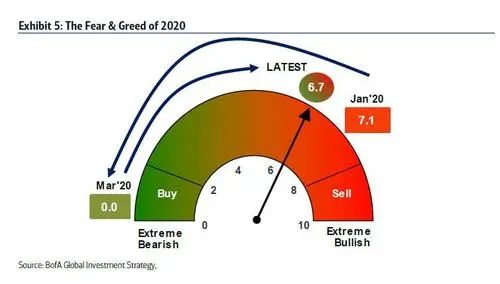
而目前投资者情绪已经基本恢复,特别是在11月初宣布疫苗计划之后。美银的牛熊指标已经加速攀升至6.7,并且正在接近卖出区域。
病毒、崩溃、封锁和衰退引发了前所未有的货币和财政政策恐慌(图6);在过去的9个月里,世界各地宣布了22万亿美元的刺激计划。
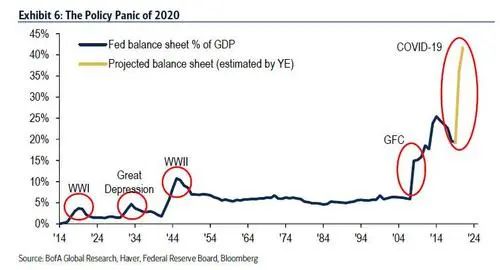
各国央行每月通过量化宽松购买逾1万亿美元金融资产,这打压了收益率、波动性和息差,成功地推动了华尔街资产价格的上涨,并缩短了经济衰退的时间。
而所宣布的14万亿美元财政刺激计划,预示着全球正从货币量化宽松向MMT(现代货币理论)的长期转变;目前,全球债务规模已达到创纪录的277万亿美元,债务收益率也处于5000年以来的最低水平(全球负收益率债务已达到18万亿美元)。
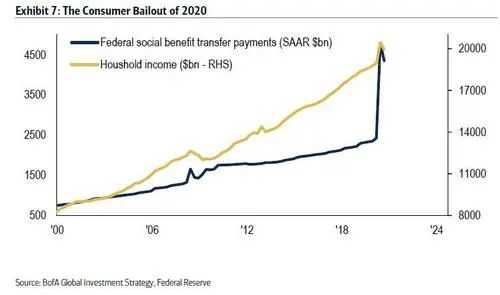
2020年,美国政府直接向家庭部门转移了2万亿美元(图7),面对病毒和失业,消费者支出可谓英勇无畏。但华尔街和主流金融机构现在对政府救助的依赖已成习惯。
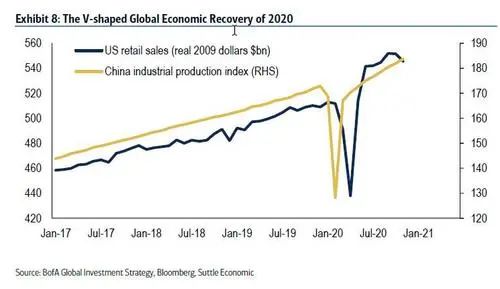
政策刺激导致华尔街出现了史诗般的反弹行情,并在2020年下半年走出了戏剧性的V型经济复苏。
复苏是由中国引领的,中国的工业生产(图8)和出口迅速恢复到新冠疫情前的水平,但对许多人来说,更值得注意的是美国消费支出的反弹(最新零售额比1月20日高出320亿美元)。
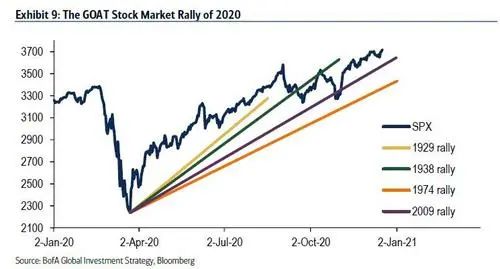
自3月20日的低点以来,全球股市市值已飙升40万亿美元,至逾100万亿美元。3月20日低点以来的反弹幅度(图9)也已经超过了过去一个世纪以来最大的四次反弹(1929年、1938年、1974年和2009年)。
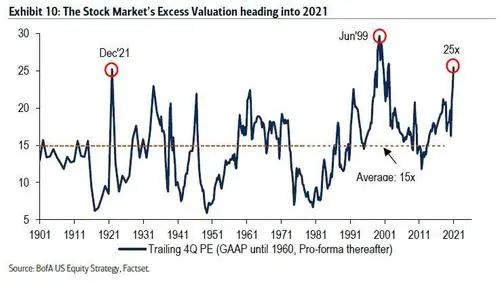
华尔街对2021年的乐观态度意味着标普500指数的市盈率将超过25倍(图10),仅在1921年和1999年超过了该水平。
股市将在未来几年大幅上涨的催化剂有很多——“不要与美联储对抗”的共识,MMT(现代货币理论),由科技主导的长期生产率……但最可信的催化剂仍然是老式的泡沫。
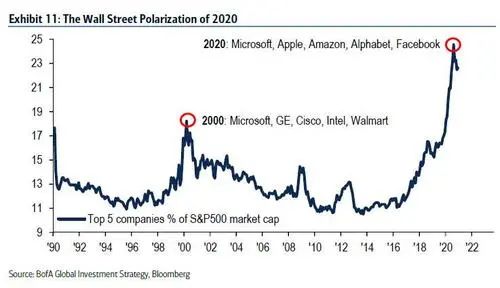
2020年华尔街资产的回报也呈现了明显的两级分化:标普500指数的前5大公司市值已占该指数的25%,令人惊叹(图11)。
到2020年尾声,反弹的类型、行业、规模和地区都有所扩大。年底时,多数股票和信贷投资者采用了一种流行的“杠铃”投资法则——即将投资集中到短期证券和长期证券两种工具上,随利率变动而不断调整两者之间资金分配比例的一种投资策略。
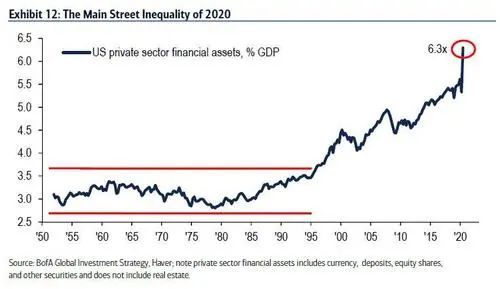
而最后,这场大流行病显然在2020年加剧了不平等——金融资产相对于经济的比值达到了6.3倍的历史最高水平(图12)。
如果没有一场大变革,这种状况不会得到改善,因为未来几年的特征将是更大的政府、美元贬值、政策从货币和量化宽松转向财政和MMT,所有这些都试图提高劳动力相对于资本的价格,但结果将适得其反。正如Hartnett所言,2020年不仅是新冠肺炎大流行年,也将会作为通胀和利率的长期低点而被人们牢记。














文章评论
The most exciting new trains coming in 2025
<a href=https://vc.ru/shopaholic/1731691-promokody-yandeks-puteshestviya-na-pervyi-zakaz-top-10-luchshie-skidki-yanvarya-2025>промокод яндекс путешествия с баллами</a>
Amazing adventures, extraordinary landscapes and fabulous cuisine — the world’s greatest railway journeys are an unforgettable experience that can immerse you in the culture of a new country.
Demand for luxury “land cruise” trains with five-star hotel-style accommodation is booming. 2025 will see several new trains take to the rails for the first time, offering new opportunities to explore Italy, France, Saudi Arabia and the United Kingdom.
But the best railway journeys don’t have to be the most expensive. There’s an ever-evolving world of train trips out there. Here are some of the key developments in the coming year
Two of Europe’s great capitals are now linked by their first direct high-speed train connection. Germany’s Deutsche Bahn introduced a daytime InterCity Express (ICE) service between Paris and Berlin on December 16 and is planning to add a second route between the two capitals in 2026.
Taking advantage of its new fleet of 200 mph (322 kph) ICE3neo trains, the once-a-day service takes around eight hours in each direction, also serving Strasbourg, Karlsruhe and Frankfurt on its 546-mile (878-kilometer) journey.
Fares start from around $60, and each train has capacity for 444 passengers, of which 111 can enjoy the additional comfort of leather seats and at-seat refreshments in first class.
The new high-speed ICE service is the first direct daytime train between Paris and Berlin since the 1990s and complements the Nightjet sleeper service introduced in 2023.
It may not be as fast as flying — some of the journey has to use lower speed “classic” lines to bridge gaps in the European high-speed network — but it is undoubtedly a more sustainable and more stylish way to travel across Europe.
<a href="https://canadianpharmacypoint.com/">pharmacy drugstore online</a>
<a href="https://canadianpharmacypoint.com/">canadian pharmacy in canada</a>
<a href="https://canadianpharmacypoint.com/">best online drugstore</a>
Попробуйте свою удачу в лучших онлайн казино, где каждый может стать победителем.
Получайте азарт и адреналин вместе с нами, и почувствуйте вкус победы.
Сделайте свой выбор в пользу казино онлайн, и начните выигрывать уже сегодня.
Ощутите волнение в режиме реального времени, не выходя из дома.
Ставьте на победу с нашими играми, и почувствуйте себя настоящим чемпионом.
Насладитесь игровым процессом вместе с игроками со всех уголков планеты, и станьте лучшим из лучших.
Начните играть и получите ценные подарки, которые принесут вам еще больше радости и азарта.
Ощутите азарт в каждой игре казино онлайн, и погрузитесь в мир бесконечных перспектив.
Играйте в игры, недоступные где-либо еще, с минимум затрат времени и усилий.
казино онлайн беларусь <a href=https://casino-on-line.by/>казино онлайн</a> .
<a href=https://2bsgate.sbs/>блэк спрут тор</a>
<a href=https://2megagate.sbs>kraken 13 at сайт</a>
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky will meet US President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris in Washington on Thursday. Leon Neal/Getty Images
CNN
—
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s visit to the White House on Thursday could be his final chance to convince a receptive American president of his country’s war aims.
<a href=https://megaweb-13at.com>MEGA</a>
The precise details of the “victory plan” Zelensky plans to present in separate meetings to President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris are unknown, having been closely held until they are presented to the American leaders.
But according to people briefed on its broad contours, the plan reflects the Ukrainian leader’s urgent appeals for more immediate help countering Russia’s invasion. Zelensky is also poised to push for long-term security guarantees that could withstand changes in American leadership ahead of what is widely expected to be a close presidential election between Harris and former President Donald Trump.
The plan, people familiar with it said, acts as Zelensky’s response to growing war weariness even among his staunchest of western allies. It will make the case that Ukraine can still win — and does not need to cede Russian-seized territory for the fighting to end — if enough assistance is rushed in.
That includes again asking permission to fire Western provided long-range weapons deeper into Russian territory, a line Biden once was loathe to cross but which he’s recently appeared more open to as he has come under growing pressure to relent.
Even if Biden decides to allow the long-range fires, it’s unclear whether the change in policy would be announced publicly.
Biden is usually apt to take his time making decisions about providing Ukraine new capabilities. But with November’s election potentially portending a major change in American approach to the war if Trump were to win, Ukrainian officials — and many American ones — believe there is little time to waste.
megaweb4.com
https://megaweb-15at.com
Trump has claimed he will be able to “settle” the war upon taking office and has suggested he’ll end US support for Kyiv’s war effort.
“Those cities are gone, they’re gone, and we continue to give billions of dollars to a man who refused to make a deal, Zelensky. There was no deal that he could have made that wouldn’t have been better than the situation you have right now. You have a country that has been obliterated, not possible to be rebuilt,” Trump said during a campaign speech in Mint Hill, North Carolina, on Wednesday.
Comments like those have lent new weight to Thursday’s Oval Office talks, according to American and European officials, who have described an imperative to surge assistance to Ukraine while Biden is still in office.
As part of Zelensky’s visit, the US is expected to announce a major new security package, thought it will likely delay the shipping of the equipment due to inventory shortages, CNN previously reported according to two US officials. On Wednesday, the US announced a package of $375 million.
The president previewed Zelensky’s visit to the White House a day beforehand, declaring on the margins of the United Nations General Assembly his administration was “determined to ensure that Ukraine has what it needs to prevail in fight for survival.”
<a href=https://megaweb-8at.com>megaweb1.com</a>
“Tomorrow, I will announce a series of actions to accelerate support for Ukraine’s military – but we know Ukraine’s future victory is about more than what happens on the battlefield, it’s also about what Ukrainians do make the most of a free and independent future, which so many have sacrificed so much for,” he said.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky will meet US President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris in Washington on Thursday. Leon Neal/Getty Images
CNN
—
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s visit to the White House on Thursday could be his final chance to convince a receptive American president of his country’s war aims.
<a href=https://megaweb20at.com>megaweb9.com</a>
The precise details of the “victory plan” Zelensky plans to present in separate meetings to President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris are unknown, having been closely held until they are presented to the American leaders.
But according to people briefed on its broad contours, the plan reflects the Ukrainian leader’s urgent appeals for more immediate help countering Russia’s invasion. Zelensky is also poised to push for long-term security guarantees that could withstand changes in American leadership ahead of what is widely expected to be a close presidential election between Harris and former President Donald Trump.
The plan, people familiar with it said, acts as Zelensky’s response to growing war weariness even among his staunchest of western allies. It will make the case that Ukraine can still win — and does not need to cede Russian-seized territory for the fighting to end — if enough assistance is rushed in.
That includes again asking permission to fire Western provided long-range weapons deeper into Russian territory, a line Biden once was loathe to cross but which he’s recently appeared more open to as he has come under growing pressure to relent.
Even if Biden decides to allow the long-range fires, it’s unclear whether the change in policy would be announced publicly.
Biden is usually apt to take his time making decisions about providing Ukraine new capabilities. But with November’s election potentially portending a major change in American approach to the war if Trump were to win, Ukrainian officials — and many American ones — believe there is little time to waste.
мега ссылка
https://mega555kf7lsmb54yd6etzginolhxxi4ytdoma2rf77ngq5fhcnid.com
Trump has claimed he will be able to “settle” the war upon taking office and has suggested he’ll end US support for Kyiv’s war effort.
“Those cities are gone, they’re gone, and we continue to give billions of dollars to a man who refused to make a deal, Zelensky. There was no deal that he could have made that wouldn’t have been better than the situation you have right now. You have a country that has been obliterated, not possible to be rebuilt,” Trump said during a campaign speech in Mint Hill, North Carolina, on Wednesday.
Comments like those have lent new weight to Thursday’s Oval Office talks, according to American and European officials, who have described an imperative to surge assistance to Ukraine while Biden is still in office.
As part of Zelensky’s visit, the US is expected to announce a major new security package, thought it will likely delay the shipping of the equipment due to inventory shortages, CNN previously reported according to two US officials. On Wednesday, the US announced a package of $375 million.
The president previewed Zelensky’s visit to the White House a day beforehand, declaring on the margins of the United Nations General Assembly his administration was “determined to ensure that Ukraine has what it needs to prevail in fight for survival.”
<a href=https://megaweb-4at.com>mega333mq5acolj7rw726jjy6g3ihgsmnhlfuuk6cd2267jbohhc4aqd.onion</a>
“Tomorrow, I will announce a series of actions to accelerate support for Ukraine’s military – but we know Ukraine’s future victory is about more than what happens on the battlefield, it’s also about what Ukrainians do make the most of a free and independent future, which so many have sacrificed so much for,” he said.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky will meet US President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris in Washington on Thursday. Leon Neal/Getty Images
CNN
—
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s visit to the White House on Thursday could be his final chance to convince a receptive American president of his country’s war aims.
<a href=https://mega555kf7lsmb54yd6etzginolhxxi4ytdoma2rf77ngq5fhfcnid.com>megaweb19.at</a>
The precise details of the “victory plan” Zelensky plans to present in separate meetings to President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris are unknown, having been closely held until they are presented to the American leaders.
But according to people briefed on its broad contours, the plan reflects the Ukrainian leader’s urgent appeals for more immediate help countering Russia’s invasion. Zelensky is also poised to push for long-term security guarantees that could withstand changes in American leadership ahead of what is widely expected to be a close presidential election between Harris and former President Donald Trump.
The plan, people familiar with it said, acts as Zelensky’s response to growing war weariness even among his staunchest of western allies. It will make the case that Ukraine can still win — and does not need to cede Russian-seized territory for the fighting to end — if enough assistance is rushed in.
That includes again asking permission to fire Western provided long-range weapons deeper into Russian territory, a line Biden once was loathe to cross but which he’s recently appeared more open to as he has come under growing pressure to relent.
Even if Biden decides to allow the long-range fires, it’s unclear whether the change in policy would be announced publicly.
Biden is usually apt to take his time making decisions about providing Ukraine new capabilities. But with November’s election potentially portending a major change in American approach to the war if Trump were to win, Ukrainian officials — and many American ones — believe there is little time to waste.
мега сайт
https://megaweb14at.com
Trump has claimed he will be able to “settle” the war upon taking office and has suggested he’ll end US support for Kyiv’s war effort.
“Those cities are gone, they’re gone, and we continue to give billions of dollars to a man who refused to make a deal, Zelensky. There was no deal that he could have made that wouldn’t have been better than the situation you have right now. You have a country that has been obliterated, not possible to be rebuilt,” Trump said during a campaign speech in Mint Hill, North Carolina, on Wednesday.
Comments like those have lent new weight to Thursday’s Oval Office talks, according to American and European officials, who have described an imperative to surge assistance to Ukraine while Biden is still in office.
As part of Zelensky’s visit, the US is expected to announce a major new security package, thought it will likely delay the shipping of the equipment due to inventory shortages, CNN previously reported according to two US officials. On Wednesday, the US announced a package of $375 million.
The president previewed Zelensky’s visit to the White House a day beforehand, declaring on the margins of the United Nations General Assembly his administration was “determined to ensure that Ukraine has what it needs to prevail in fight for survival.”
<a href=https://megaweb13at.com>megaweb2.at</a>
“Tomorrow, I will announce a series of actions to accelerate support for Ukraine’s military – but we know Ukraine’s future victory is about more than what happens on the battlefield, it’s also about what Ukrainians do make the most of a free and independent future, which so many have sacrificed so much for,” he said.
I'm not sure exactly why but this blog is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a issue on my end? I'll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
<a href=https://abshop.com.ua/how-to-determine-headlight-sealant-quality.html>https://abshop.com.ua/how-to-determine-headlight-sealant-quality.html</a>
A year ago today, things went from bad to worse for Boeing
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kra23 cc</a>
At 5 p.m. PT on January 5, 2024, Boeing seemed like a company on the upswing. It didn’t last. Minutes later, a near-tragedy set off a full year of problems.
As Alaska Airlines flight 1282 climbed to 16,000 feet in its departure from Portland, Oregon, a door plug blew out near the rear of the plane, leaving a gaping hole in the fuselage. Phones and clothing were ripped away from passengers and sent hurtling into the night sky. Oxygen masks dropped, and the rush of air twisted seats next to the hole toward the opening.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken marketplace
Fortunately, those were among the few empty seats on the flight, and the crew got the plane on the ground without any serious injuries. The incident could have been far worse — even a fatal crash.
Not much has gone right for Boeing ever since. The company has had one misstep after another, ranging from embarrassing to horrifying. And many of the problems are poised to extend into 2025 and perhaps beyond.
The problems were capped by another Boeing crash in South Korea that killed 179 people on December 29 in what was in the year’s worst aviation disaster. The cause of the crash of a 15-year old Boeing jet flown by Korean discount carrier Jeju Air is still under investigation, and it is quite possible that Boeing will not be found liable for anything that led to the tragedy.
But unlike the Jeju crash, most of the problems of the last 12 months have clearly been Boeing’s fault.
And 2024 was the sixth straight year of serious problems for the once proud, now embattled company, starting with the 20-month grounding of its best selling plane, the 737 Max, following two fatal crashes in late 2018 and early 2019, which killed 346 people.
Still the outlook for 2024 right before the Alaska Air incident had been somewhat promising. The company had just achieved the best sales month in its history in December 2023, capping its strongest sales year since 2018.
It was believed to be on the verge of getting Federal Aviation Administration approval for two new models, the 737 Max 7 and Max 10, with airline customers eager to take delivery. Approvals and deliveries of its next generation widebody, the 777X, were believed to be close behind. Its production rate had been climbing and there were hopes that it could be on the verge of returning to profitability for the first time since 2018.
Scientists have identified an estimated 10% of all species on Earth. Here’s what they found in 2024
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken market</a>
A toothy toadstool. A vegetarian piranha with a distinctive mark. And a pygmy pipehorse floating in the Indian Ocean shallows.
These wild wonders were among the hundreds of previously unknown species of animals, plants and fungi that scientists named and described for the first time in 2024, expanding our surprisingly limited knowledge of Earth’s diversity.
“Scientists estimate that we’ve identified only one-tenth of all species on Earth,” said Dr.
Shannon Bennett, chief of science at the California Academy of Sciences, in a statement.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken вход
“While it is critical to place protections on known threatened species, we must also allocate resources towards identifying unknown species that may be just as important to the functioning of an ecosystem,” Bennett said.
Researchers connected to the institution described 138 new species in 2024, including 32 fish. One standout was a pygmy pipehorse named Cylix nkosi. The seahorse relative was originally found in 2021 in the cool temperate waters surrounding the North Island of New Zealand, but the species described this year was discovered in the subtropical waters off South Africa, expanding the known range of this group to the Indian Ocean
“South African reefs present notoriously difficult diving conditions with rough weather and intense, choppy waves — we knew we only had one dive to find it,” underwater photographer and marine biologist Richard Smith said in a statement.
“This species is also quite cryptic, about the size of a golf tee, but luckily we spotted a female camouflaged against some sponges about a mile offshore on the sandy ocean floor.”
The researchers involved in describing the new species chose nkosi as its name. A reference to the local Zulu word for “chief,” the name reflects the species’ crown-like head shape and acknowledges South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province where it was found.
Most plane crashes are ‘survivable’
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken сайт</a>
First, the good news. “The vast majority of aircraft accidents are survivable, and the majority of people in accidents survive,” says Galea. Since 1988, aircraft — and the seats inside them — must be built to withstand an impact of up to 16G, or g-force up to 16 times the force of gravity. That means, he says, that in most incidents, “it’s possible to survive the trauma of the impact of the crash.”
For instance, he classes the initial Jeju Air incident as survivable — an assumed bird strike, engine loss and belly landing on the runway, without functioning landing gear. “Had it not smashed into the concrete reinforced obstacle at the end of the runway, it’s quite possible the majority, if not everyone, could have survived,” he says.
The Azerbaijan Airlines crash, on the other hand, he classes as a non-survivable accident, and calls it a “miracle” that anyone made it out alive.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken shop
Most aircraft involved in accidents, however, are not — as suspicion is growing over the Azerbaijan crash — shot out of the sky.
And with modern planes built to withstand impacts and slow the spread of fire, Galea puts the chances of surviving a “survivable” accident at at least 90%.
Instead, he says, what makes the difference between life and death in most modern accidents is how fast passengers can evacuate.
Aircraft today must show that they can be evacuated in 90 seconds in order to gain certification. But a theoretical evacuation — practiced with volunteers at the manufacturers’ premises — is very different from the reality of a panicked public onboard a jet that has just crash-landed.
Galea, an evacuation expert, has conducted research for the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) looking at the most “survivable” seats on a plane. His landmark research, conducted over several years in the early 2000s, looked at how passengers and crew behaved during a post-crash evacuation, rather than looking at the crashes themselves. By compiling data from 1,917 passengers and 155 crew involved in 105 accidents from 1977 to 1999, his team created a database of human behavior around plane crashes.
His analysis of which exits passengers actually used “shattered many myths about aircraft evacuation,” he says. “Prior to my study, it was believed that passengers tend to use their boarding exit because it was the most familiar, and that passengers tend to go forward. My analysis of the data demonstrated that none of these myths were supported by the evidence.”
The survivors of recent crashes were sitting at the back of the plane. What does that tell us about airplane safety?
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken официальный сайт</a>
Look at the photos of the two fatal air crashes of the last two weeks, and amid the horror and the anguish, one thought might come to mind for frequent flyers.
The old frequent-flyer adage is that sitting at the back of the plane is a safer place to be than at the front — and the wreckage of both Azerbaijan Airlines flight 8243 and Jeju Air flight 2216 seem to bear that out.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken ссылка
The 29 survivors of the Azeri crash were all sitting at the back of the plane, which split into two, leaving the rear half largely intact. The sole survivors of the South Korean crash, meanwhile, were the two flight attendants in their jumpseats in the very tail of the plane.
So is that old adage — and the dark humor jokes about first and business class seats being good until there’s a problem with the plane — right after all?
In 2015, TIME Magazine reporters wrote that they had combed through the records of all US plane crashes with both fatalities and survivors from 1985 to 2000, and found in a meta-analysis that seats in the back third of the aircraft had a 32% fatality rate overall, compared with 38% in the front third and 39% in the middle third.
Even better, they found, were middle seats in that back third of the cabin, with a 28% fatality rate. The “worst” seats were aisles in the middle third of the aircraft, with a 44% fatality rate.
But does that still hold true in 2024?
According to aviation safety experts, it’s an old wives’ tale.
“There isn’t any data that shows a correlation of seating to survivability,” says Hassan Shahidi, president of the Flight Safety Foundation. “Every accident is different.”
“If we’re talking about a fatal crash, then there is almost no difference where one sits,” says Cheng-Lung Wu, associate professor at the School of Aviation of the University of New South Wales, Sydney.
Ed Galea, professor of fire safety engineering at London’s University of Greenwich, who has conducted landmark studies on plane crash evacuations, warns, “There is no magic safest seat.”
Chile’s President Boric leads journey to South Pole in historic trip
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>kraken shop</a>
Chile’s President Gabriel Boric travelled to Antarctica’s South Pole on Friday, a place where no other Latin American president has set foot, according to the Chilean government.
Boric led the historic two-day trip, named Operation Pole Star III, to extend the environmental monitoring of pollutants on Antarctica, Chile’s government said in a statement.
He travelled with scientists, armed forces commanders and government ministers from the Chilean capital of Santiago to Punta Arenas, a city in southern Chile, public broadcaster Television Nacional de Chile (TVN) reported. From there, they made several stops before finally reaching the US-run Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, according to TVN.
https://kra23s.cc
kraken shop
Chile is one of seven countries that has a territorial claim in Antarctica, alongside Argentina, Australia, France, New Zealand, Norway and the United Kingdom.
It is also a signatory of the Antarctic Treaty, which dictates that the continent may only be used for peaceful and scientific purposes.
While Chile has historically carried out scientific activity in Antarctica’s northern sector, the country’s government is now hoping to expand research into the west of the continent, its statement said.
Boric called his trip to the South Pole an “honor” and a source of pride, TVN reported.
“This is a milestone for us. It is the first time a Chilean and Latin American President has visited the South Pole,” he said, according to TVN.
What New Glenn will do
In some ways, New Glenn has already made its mark on the launch industry. Blue Origin has for years pitched the rocket to compete with both SpaceX and United Launch Alliance — a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin that buys engines from Blue Origin — for lucrative military launch contracts.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>площадка omg</a>
The US Space Force selected Blue Origin, ULA and SpaceX in June to compete for $5.6 billion worth of Pentagon contracts for national security missions slated to launch over the next four years.
Blue Origin also has deals with several commercial companies to launch satellites. The contracts include plans to help deploy Amazon’s Kuiper internet satellites and a recently inked deal with AST SpaceMobile to help launch the Midland, Texas-based company’s space-based cellular broadband network.
New Glenn could also be instrumental in building Blue Origin’s planned space station, called Orbital Reef. Blue Origin and it commercial partners, including Sierra Space and Boeing, among others, hope the station will one day provide a new destination for astronauts as the International Space Station is phased out of service.
https://omgprice10.com
omg онион
New Glenn vs. other powerful rockets
New Glenn packs significant power. Dubbed a “heavy-lift” vehicle, its capabilities lie between SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and the more powerful Falcon Heavy launch vehicle.
SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9, for example, can haul up to 22.8 metric tons (50,265 pounds) to space. While New Glenn is capable of carrying about double that mass, it may also be roughly the same price as a Falcon 9: reportedly around $60 million to $70 million per launch.
“I think in order to compete with Falcon 9, you have to go head-to-head or better on price,” said Caleb Henry, the director of research at Quilty Space, which provides data and analysis about the space sector.
The question, however, is whether Blue Origin will be able to sustain a competitive price point, Henry added.
Still, one feature that makes New Glenn stand out is its large payload fairing, or nose cone. The component protects the cargo bay and is a whopping 23 feet (7 meters) wide — nearly 6 feet (2 meters) larger than that of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy.
Henry said Blue Origin likely opted to outfit New Glenn with such a large fairing in order to help fulfill Bezos’ vision of the future.
What’s on board this flight
Blue Origin had planned to launch a pair of Mars-bound satellites on behalf of NASA for the first flight of New Glenn.
But delays with the rocket’s development prompted the space agency to change course, moving that flight to this spring at the earliest. So for this inaugural flight, Blue Origin opted to instead fly a “demonstrator” that will test technology needed for the company’s proposed Blue Ring spacecraft — which will aim to serve as a sort of in-space rideshare vehicle, dragging satellites deeper into space when needed.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>омг омг</a>
The demonstrator on this New Glenn flight will remain aboard the rocket for the entire six-hour flight, Blue Origin said, and it will validate “communications capabilities from orbit to ground” as well as “test its in-space telemetry, tracking and command hardware, and ground-based radiometric tracking.”
The Blue Ring Pathfinder demonstrator is part of a deal Blue Origin inked with the US Department of Defense’s Defense Innovation Unit.
https://omgprice10.com
omg omg onion
Why Blue Origin wants to reuse rockets
Similar to SpaceX, Blue Origin is aiming to recover and refly its first-stage rocket boosters in a bid to make launches less expensive.
“Reusability is integral to radically reducing cost-per-launch,” the company said in a recent news release, using the same oft-repeated sentiment that SpaceX has touted since it began landing rocket boosters in 2015.
Bezos, however, has acknowledged the importance of reusing rocket parts since he founded the company in 2000 — two years before Musk established SpaceX. And the company has already developed its suborbital New Shepard tourism rocket to be reusable.
“It’s not a copy cat game,” Henry said. “Blue Origin has been pursuing reusable vehicles since before reusable vehicles were cool. Now it’s much more of a mainstream idea (because of SpaceX). The difference is that it’s taken Blue Origin so much longer to get to orbit.”
If successful, returning the New Glenn rocket booster for a safe landing will be a stunning feat. After expending most of its fuel to propel the rocket’s upper stage to space, the first-stage booster will need to make a clean separation. The booster must then maneuver with pinpoint guidance and reignite its engines with precision timing to avoid crashing into the ocean or the Jacklyn recovery platform.
Scientists have identified an estimated 10% of all species on Earth. Here’s what they found in 2024
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>кракен</a>
A toothy toadstool. A vegetarian piranha with a distinctive mark. And a pygmy pipehorse floating in the Indian Ocean shallows.
These wild wonders were among the hundreds of previously unknown species of animals, plants and fungi that scientists named and described for the first time in 2024, expanding our surprisingly limited knowledge of Earth’s diversity.
“Scientists estimate that we’ve identified only one-tenth of all species on Earth,” said Dr.
Shannon Bennett, chief of science at the California Academy of Sciences, in a statement.
https://kra23c.cc
кракен онион
“While it is critical to place protections on known threatened species, we must also allocate resources towards identifying unknown species that may be just as important to the functioning of an ecosystem,” Bennett said.
Researchers connected to the institution described 138 new species in 2024, including 32 fish. One standout was a pygmy pipehorse named Cylix nkosi. The seahorse relative was originally found in 2021 in the cool temperate waters surrounding the North Island of New Zealand, but the species described this year was discovered in the subtropical waters off South Africa, expanding the known range of this group to the Indian Ocean
“South African reefs present notoriously difficult diving conditions with rough weather and intense, choppy waves — we knew we only had one dive to find it,” underwater photographer and marine biologist Richard Smith said in a statement.
“This species is also quite cryptic, about the size of a golf tee, but luckily we spotted a female camouflaged against some sponges about a mile offshore on the sandy ocean floor.”
The researchers involved in describing the new species chose nkosi as its name. A reference to the local Zulu word for “chief,” the name reflects the species’ crown-like head shape and acknowledges South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province where it was found.
Most plane crashes are ‘survivable’
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken сайт</a>
First, the good news. “The vast majority of aircraft accidents are survivable, and the majority of people in accidents survive,” says Galea. Since 1988, aircraft — and the seats inside them — must be built to withstand an impact of up to 16G, or g-force up to 16 times the force of gravity. That means, he says, that in most incidents, “it’s possible to survive the trauma of the impact of the crash.”
For instance, he classes the initial Jeju Air incident as survivable — an assumed bird strike, engine loss and belly landing on the runway, without functioning landing gear. “Had it not smashed into the concrete reinforced obstacle at the end of the runway, it’s quite possible the majority, if not everyone, could have survived,” he says.
The Azerbaijan Airlines crash, on the other hand, he classes as a non-survivable accident, and calls it a “miracle” that anyone made it out alive.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken onion
Most aircraft involved in accidents, however, are not — as suspicion is growing over the Azerbaijan crash — shot out of the sky.
And with modern planes built to withstand impacts and slow the spread of fire, Galea puts the chances of surviving a “survivable” accident at at least 90%.
Instead, he says, what makes the difference between life and death in most modern accidents is how fast passengers can evacuate.
Aircraft today must show that they can be evacuated in 90 seconds in order to gain certification. But a theoretical evacuation — practiced with volunteers at the manufacturers’ premises — is very different from the reality of a panicked public onboard a jet that has just crash-landed.
Galea, an evacuation expert, has conducted research for the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) looking at the most “survivable” seats on a plane. His landmark research, conducted over several years in the early 2000s, looked at how passengers and crew behaved during a post-crash evacuation, rather than looking at the crashes themselves. By compiling data from 1,917 passengers and 155 crew involved in 105 accidents from 1977 to 1999, his team created a database of human behavior around plane crashes.
His analysis of which exits passengers actually used “shattered many myths about aircraft evacuation,” he says. “Prior to my study, it was believed that passengers tend to use their boarding exit because it was the most familiar, and that passengers tend to go forward. My analysis of the data demonstrated that none of these myths were supported by the evidence.”
The survivors of recent crashes were sitting at the back of the plane. What does that tell us about airplane safety?
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken даркнет</a>
Look at the photos of the two fatal air crashes of the last two weeks, and amid the horror and the anguish, one thought might come to mind for frequent flyers.
The old frequent-flyer adage is that sitting at the back of the plane is a safer place to be than at the front — and the wreckage of both Azerbaijan Airlines flight 8243 and Jeju Air flight 2216 seem to bear that out.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken
The 29 survivors of the Azeri crash were all sitting at the back of the plane, which split into two, leaving the rear half largely intact. The sole survivors of the South Korean crash, meanwhile, were the two flight attendants in their jumpseats in the very tail of the plane.
So is that old adage — and the dark humor jokes about first and business class seats being good until there’s a problem with the plane — right after all?
In 2015, TIME Magazine reporters wrote that they had combed through the records of all US plane crashes with both fatalities and survivors from 1985 to 2000, and found in a meta-analysis that seats in the back third of the aircraft had a 32% fatality rate overall, compared with 38% in the front third and 39% in the middle third.
Even better, they found, were middle seats in that back third of the cabin, with a 28% fatality rate. The “worst” seats were aisles in the middle third of the aircraft, with a 44% fatality rate.
But does that still hold true in 2024?
According to aviation safety experts, it’s an old wives’ tale.
“There isn’t any data that shows a correlation of seating to survivability,” says Hassan Shahidi, president of the Flight Safety Foundation. “Every accident is different.”
“If we’re talking about a fatal crash, then there is almost no difference where one sits,” says Cheng-Lung Wu, associate professor at the School of Aviation of the University of New South Wales, Sydney.
Ed Galea, professor of fire safety engineering at London’s University of Greenwich, who has conducted landmark studies on plane crash evacuations, warns, “There is no magic safest seat.”
On a long-dormant pad in Florida, a rocket that could challenge SpaceX’s dominance is poised to launch
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>кракен вход</a>
On a Florida launchpad that has been dormant for almost two decades, a new, roughly 320-foot (98-meter) rocket — developed by Jeff Bezos’ company Blue Origin — is poised for its maiden flight.
The uncrewed launch vehicle, called New Glenn, will mark Blue Origin’s first attempt to send a rocket to orbit, a feat necessary if the company hopes to chip away at SpaceX’s long-held dominance in the industry.
New Glenn is set to lift off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station as early as next week.
https://kra23s.cc
кракен
The rocket, which stands about as tall as a 30-story building, consists of several parts: The first-stage rocket booster gives the initial thrust at liftoff. Atop the booster is an upper rocket stage that includes a cargo bay protected by a nose cone that will house experimental technology for this mission.
And, in an attempt to replicate the success that SpaceX has found reusing rocket boosters over the past decade, Blue Origin will also aim to guide New Glenn’s first-stage rocket booster back to a safe landing on a seafaring platform — named Jacklyn for Bezos’ mother — minutes after takeoff.
Like SpaceX, Blue Origin will seek to recover, refurbish and reuse first-stage rocket boosters to drive down costs.
For this inaugural mission, a smooth flight is not guaranteed.
But the eventual success of New Glenn, named after storied NASA astronaut John Glenn, is instrumental to some of Blue Origin’s most ambitious goals.
The rocket could one day power national security launches, haul Amazon internet satellites to space and even help in the construction of a space station that Blue Origin is developing with commercial partners.
A year ago today, things went from bad to worse for Boeing
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken ссылка</a>
At 5 p.m. PT on January 5, 2024, Boeing seemed like a company on the upswing. It didn’t last. Minutes later, a near-tragedy set off a full year of problems.
As Alaska Airlines flight 1282 climbed to 16,000 feet in its departure from Portland, Oregon, a door plug blew out near the rear of the plane, leaving a gaping hole in the fuselage. Phones and clothing were ripped away from passengers and sent hurtling into the night sky. Oxygen masks dropped, and the rush of air twisted seats next to the hole toward the opening.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken вход
Fortunately, those were among the few empty seats on the flight, and the crew got the plane on the ground without any serious injuries. The incident could have been far worse — even a fatal crash.
Not much has gone right for Boeing ever since. The company has had one misstep after another, ranging from embarrassing to horrifying. And many of the problems are poised to extend into 2025 and perhaps beyond.
The problems were capped by another Boeing crash in South Korea that killed 179 people on December 29 in what was in the year’s worst aviation disaster. The cause of the crash of a 15-year old Boeing jet flown by Korean discount carrier Jeju Air is still under investigation, and it is quite possible that Boeing will not be found liable for anything that led to the tragedy.
But unlike the Jeju crash, most of the problems of the last 12 months have clearly been Boeing’s fault.
And 2024 was the sixth straight year of serious problems for the once proud, now embattled company, starting with the 20-month grounding of its best selling plane, the 737 Max, following two fatal crashes in late 2018 and early 2019, which killed 346 people.
Still the outlook for 2024 right before the Alaska Air incident had been somewhat promising. The company had just achieved the best sales month in its history in December 2023, capping its strongest sales year since 2018.
It was believed to be on the verge of getting Federal Aviation Administration approval for two new models, the 737 Max 7 and Max 10, with airline customers eager to take delivery. Approvals and deliveries of its next generation widebody, the 777X, were believed to be close behind. Its production rate had been climbing and there were hopes that it could be on the verge of returning to profitability for the first time since 2018.
What New Glenn will do
In some ways, New Glenn has already made its mark on the launch industry. Blue Origin has for years pitched the rocket to compete with both SpaceX and United Launch Alliance — a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin that buys engines from Blue Origin — for lucrative military launch contracts.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>omg даркнет</a>
The US Space Force selected Blue Origin, ULA and SpaceX in June to compete for $5.6 billion worth of Pentagon contracts for national security missions slated to launch over the next four years.
Blue Origin also has deals with several commercial companies to launch satellites. The contracts include plans to help deploy Amazon’s Kuiper internet satellites and a recently inked deal with AST SpaceMobile to help launch the Midland, Texas-based company’s space-based cellular broadband network.
New Glenn could also be instrumental in building Blue Origin’s planned space station, called Orbital Reef. Blue Origin and it commercial partners, including Sierra Space and Boeing, among others, hope the station will one day provide a new destination for astronauts as the International Space Station is phased out of service.
https://omgprice10.com
omg вход
New Glenn vs. other powerful rockets
New Glenn packs significant power. Dubbed a “heavy-lift” vehicle, its capabilities lie between SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and the more powerful Falcon Heavy launch vehicle.
SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9, for example, can haul up to 22.8 metric tons (50,265 pounds) to space. While New Glenn is capable of carrying about double that mass, it may also be roughly the same price as a Falcon 9: reportedly around $60 million to $70 million per launch.
“I think in order to compete with Falcon 9, you have to go head-to-head or better on price,” said Caleb Henry, the director of research at Quilty Space, which provides data and analysis about the space sector.
The question, however, is whether Blue Origin will be able to sustain a competitive price point, Henry added.
Still, one feature that makes New Glenn stand out is its large payload fairing, or nose cone. The component protects the cargo bay and is a whopping 23 feet (7 meters) wide — nearly 6 feet (2 meters) larger than that of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy.
Henry said Blue Origin likely opted to outfit New Glenn with such a large fairing in order to help fulfill Bezos’ vision of the future.
What’s on board this flight
Blue Origin had planned to launch a pair of Mars-bound satellites on behalf of NASA for the first flight of New Glenn.
But delays with the rocket’s development prompted the space agency to change course, moving that flight to this spring at the earliest. So for this inaugural flight, Blue Origin opted to instead fly a “demonstrator” that will test technology needed for the company’s proposed Blue Ring spacecraft — which will aim to serve as a sort of in-space rideshare vehicle, dragging satellites deeper into space when needed.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>omg тор браузер</a>
The demonstrator on this New Glenn flight will remain aboard the rocket for the entire six-hour flight, Blue Origin said, and it will validate “communications capabilities from orbit to ground” as well as “test its in-space telemetry, tracking and command hardware, and ground-based radiometric tracking.”
The Blue Ring Pathfinder demonstrator is part of a deal Blue Origin inked with the US Department of Defense’s Defense Innovation Unit.
https://omgprice10.com
omg официальный сайт
Why Blue Origin wants to reuse rockets
Similar to SpaceX, Blue Origin is aiming to recover and refly its first-stage rocket boosters in a bid to make launches less expensive.
“Reusability is integral to radically reducing cost-per-launch,” the company said in a recent news release, using the same oft-repeated sentiment that SpaceX has touted since it began landing rocket boosters in 2015.
Bezos, however, has acknowledged the importance of reusing rocket parts since he founded the company in 2000 — two years before Musk established SpaceX. And the company has already developed its suborbital New Shepard tourism rocket to be reusable.
“It’s not a copy cat game,” Henry said. “Blue Origin has been pursuing reusable vehicles since before reusable vehicles were cool. Now it’s much more of a mainstream idea (because of SpaceX). The difference is that it’s taken Blue Origin so much longer to get to orbit.”
If successful, returning the New Glenn rocket booster for a safe landing will be a stunning feat. After expending most of its fuel to propel the rocket’s upper stage to space, the first-stage booster will need to make a clean separation. The booster must then maneuver with pinpoint guidance and reignite its engines with precision timing to avoid crashing into the ocean or the Jacklyn recovery platform.
Scientists have identified an estimated 10% of all species on Earth. Here’s what they found in 2024
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken вход</a>
A toothy toadstool. A vegetarian piranha with a distinctive mark. And a pygmy pipehorse floating in the Indian Ocean shallows.
These wild wonders were among the hundreds of previously unknown species of animals, plants and fungi that scientists named and described for the first time in 2024, expanding our surprisingly limited knowledge of Earth’s diversity.
“Scientists estimate that we’ve identified only one-tenth of all species on Earth,” said Dr.
Shannon Bennett, chief of science at the California Academy of Sciences, in a statement.
https://kra23c.cc
Кракен даркнет
“While it is critical to place protections on known threatened species, we must also allocate resources towards identifying unknown species that may be just as important to the functioning of an ecosystem,” Bennett said.
Researchers connected to the institution described 138 new species in 2024, including 32 fish. One standout was a pygmy pipehorse named Cylix nkosi. The seahorse relative was originally found in 2021 in the cool temperate waters surrounding the North Island of New Zealand, but the species described this year was discovered in the subtropical waters off South Africa, expanding the known range of this group to the Indian Ocean
“South African reefs present notoriously difficult diving conditions with rough weather and intense, choppy waves — we knew we only had one dive to find it,” underwater photographer and marine biologist Richard Smith said in a statement.
“This species is also quite cryptic, about the size of a golf tee, but luckily we spotted a female camouflaged against some sponges about a mile offshore on the sandy ocean floor.”
The researchers involved in describing the new species chose nkosi as its name. A reference to the local Zulu word for “chief,” the name reflects the species’ crown-like head shape and acknowledges South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province where it was found.
Most plane crashes are ‘survivable’
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kra25 cc</a>
First, the good news. “The vast majority of aircraft accidents are survivable, and the majority of people in accidents survive,” says Galea. Since 1988, aircraft — and the seats inside them — must be built to withstand an impact of up to 16G, or g-force up to 16 times the force of gravity. That means, he says, that in most incidents, “it’s possible to survive the trauma of the impact of the crash.”
For instance, he classes the initial Jeju Air incident as survivable — an assumed bird strike, engine loss and belly landing on the runway, without functioning landing gear. “Had it not smashed into the concrete reinforced obstacle at the end of the runway, it’s quite possible the majority, if not everyone, could have survived,” he says.
The Azerbaijan Airlines crash, on the other hand, he classes as a non-survivable accident, and calls it a “miracle” that anyone made it out alive.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken ссылка
Most aircraft involved in accidents, however, are not — as suspicion is growing over the Azerbaijan crash — shot out of the sky.
And with modern planes built to withstand impacts and slow the spread of fire, Galea puts the chances of surviving a “survivable” accident at at least 90%.
Instead, he says, what makes the difference between life and death in most modern accidents is how fast passengers can evacuate.
Aircraft today must show that they can be evacuated in 90 seconds in order to gain certification. But a theoretical evacuation — practiced with volunteers at the manufacturers’ premises — is very different from the reality of a panicked public onboard a jet that has just crash-landed.
Galea, an evacuation expert, has conducted research for the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) looking at the most “survivable” seats on a plane. His landmark research, conducted over several years in the early 2000s, looked at how passengers and crew behaved during a post-crash evacuation, rather than looking at the crashes themselves. By compiling data from 1,917 passengers and 155 crew involved in 105 accidents from 1977 to 1999, his team created a database of human behavior around plane crashes.
His analysis of which exits passengers actually used “shattered many myths about aircraft evacuation,” he says. “Prior to my study, it was believed that passengers tend to use their boarding exit because it was the most familiar, and that passengers tend to go forward. My analysis of the data demonstrated that none of these myths were supported by the evidence.”
The survivors of recent crashes were sitting at the back of the plane. What does that tell us about airplane safety?
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>Кракен тор</a>
Look at the photos of the two fatal air crashes of the last two weeks, and amid the horror and the anguish, one thought might come to mind for frequent flyers.
The old frequent-flyer adage is that sitting at the back of the plane is a safer place to be than at the front — and the wreckage of both Azerbaijan Airlines flight 8243 and Jeju Air flight 2216 seem to bear that out.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken войти
The 29 survivors of the Azeri crash were all sitting at the back of the plane, which split into two, leaving the rear half largely intact. The sole survivors of the South Korean crash, meanwhile, were the two flight attendants in their jumpseats in the very tail of the plane.
So is that old adage — and the dark humor jokes about first and business class seats being good until there’s a problem with the plane — right after all?
In 2015, TIME Magazine reporters wrote that they had combed through the records of all US plane crashes with both fatalities and survivors from 1985 to 2000, and found in a meta-analysis that seats in the back third of the aircraft had a 32% fatality rate overall, compared with 38% in the front third and 39% in the middle third.
Even better, they found, were middle seats in that back third of the cabin, with a 28% fatality rate. The “worst” seats were aisles in the middle third of the aircraft, with a 44% fatality rate.
But does that still hold true in 2024?
According to aviation safety experts, it’s an old wives’ tale.
“There isn’t any data that shows a correlation of seating to survivability,” says Hassan Shahidi, president of the Flight Safety Foundation. “Every accident is different.”
“If we’re talking about a fatal crash, then there is almost no difference where one sits,” says Cheng-Lung Wu, associate professor at the School of Aviation of the University of New South Wales, Sydney.
Ed Galea, professor of fire safety engineering at London’s University of Greenwich, who has conducted landmark studies on plane crash evacuations, warns, “There is no magic safest seat.”
On a long-dormant pad in Florida, a rocket that could challenge SpaceX’s dominance is poised to launch
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>кракен</a>
On a Florida launchpad that has been dormant for almost two decades, a new, roughly 320-foot (98-meter) rocket — developed by Jeff Bezos’ company Blue Origin — is poised for its maiden flight.
The uncrewed launch vehicle, called New Glenn, will mark Blue Origin’s first attempt to send a rocket to orbit, a feat necessary if the company hopes to chip away at SpaceX’s long-held dominance in the industry.
New Glenn is set to lift off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station as early as next week.
https://kra23s.cc
kraken tor
The rocket, which stands about as tall as a 30-story building, consists of several parts: The first-stage rocket booster gives the initial thrust at liftoff. Atop the booster is an upper rocket stage that includes a cargo bay protected by a nose cone that will house experimental technology for this mission.
And, in an attempt to replicate the success that SpaceX has found reusing rocket boosters over the past decade, Blue Origin will also aim to guide New Glenn’s first-stage rocket booster back to a safe landing on a seafaring platform — named Jacklyn for Bezos’ mother — minutes after takeoff.
Like SpaceX, Blue Origin will seek to recover, refurbish and reuse first-stage rocket boosters to drive down costs.
For this inaugural mission, a smooth flight is not guaranteed.
But the eventual success of New Glenn, named after storied NASA astronaut John Glenn, is instrumental to some of Blue Origin’s most ambitious goals.
The rocket could one day power national security launches, haul Amazon internet satellites to space and even help in the construction of a space station that Blue Origin is developing with commercial partners.
Chile’s President Boric leads journey to South Pole in historic trip
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>Площадка кракен</a>
Chile’s President Gabriel Boric travelled to Antarctica’s South Pole on Friday, a place where no other Latin American president has set foot, according to the Chilean government.
Boric led the historic two-day trip, named Operation Pole Star III, to extend the environmental monitoring of pollutants on Antarctica, Chile’s government said in a statement.
He travelled with scientists, armed forces commanders and government ministers from the Chilean capital of Santiago to Punta Arenas, a city in southern Chile, public broadcaster Television Nacional de Chile (TVN) reported. From there, they made several stops before finally reaching the US-run Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, according to TVN.
https://kra23s.cc
kraken тор
Chile is one of seven countries that has a territorial claim in Antarctica, alongside Argentina, Australia, France, New Zealand, Norway and the United Kingdom.
It is also a signatory of the Antarctic Treaty, which dictates that the continent may only be used for peaceful and scientific purposes.
While Chile has historically carried out scientific activity in Antarctica’s northern sector, the country’s government is now hoping to expand research into the west of the continent, its statement said.
Boric called his trip to the South Pole an “honor” and a source of pride, TVN reported.
“This is a milestone for us. It is the first time a Chilean and Latin American President has visited the South Pole,” he said, according to TVN.
New Glenn’s first flight
Blue Origin formally announced the development of New Glenn — which aims to outpower SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets and haul spacecraft up to 45 metric tons (99,200 pounds) to orbit — in 2016.
<a href=https://kra23att.cc>Кракен даркнет</a>
The vehicle is long overdue, as the company previously targeted 2020 for its first launch.
Delays, however, are common in the aerospace industry. And the debut flight of a new vehicle is almost always significantly behind schedule.
Rocket companies also typically take a conservative approach to the first liftoff, launching dummy payloads such as hunks of metal or, as was the case with SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy debut in 2018, an old cherry red sports car.
https://kra23att.cc
kraken зеркало
Blue Origin has also branded itself as a company that aims to take a slow, diligent approach to rocket development that doesn’t “cut any corners,” according to Bezos, who founded Blue Origin and funds the company.
The company’s mascot is a tortoise, paying homage to “The Tortoise and the Hare” fable that made the “slow and steady wins the race” mantra a childhood staple.
“We believe slow is smooth and smooth is fast,” Bezos said in 2016. Those comments could be seen as an attempt to position Blue Origin as the anti-SpaceX, which is known to embrace speed and trial-and-error over slow, meticulous development processes.
But SpaceX has certainly won the race to orbit. The company’s first orbital rocket, the Falcon 1, made a successful launch in September 2008. The company has deployed hundreds of missions to orbit since then.
And while SpaceX routinely destroys rockets during test flights as it begins developing a new rocket, the company has a solid track record for operational missions. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, for example, has experienced two in-flight failures and one launchpad explosion but no catastrophic events during human missions.
What’s on board this flight
Blue Origin had planned to launch a pair of Mars-bound satellites on behalf of NASA for the first flight of New Glenn.
But delays with the rocket’s development prompted the space agency to change course, moving that flight to this spring at the earliest. So for this inaugural flight, Blue Origin opted to instead fly a “demonstrator” that will test technology needed for the company’s proposed Blue Ring spacecraft — which will aim to serve as a sort of in-space rideshare vehicle, dragging satellites deeper into space when needed.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>омг вход</a>
The demonstrator on this New Glenn flight will remain aboard the rocket for the entire six-hour flight, Blue Origin said, and it will validate “communications capabilities from orbit to ground” as well as “test its in-space telemetry, tracking and command hardware, and ground-based radiometric tracking.”
The Blue Ring Pathfinder demonstrator is part of a deal Blue Origin inked with the US Department of Defense’s Defense Innovation Unit.
https://omgprice10.com
зайти на омг
Why Blue Origin wants to reuse rockets
Similar to SpaceX, Blue Origin is aiming to recover and refly its first-stage rocket boosters in a bid to make launches less expensive.
“Reusability is integral to radically reducing cost-per-launch,” the company said in a recent news release, using the same oft-repeated sentiment that SpaceX has touted since it began landing rocket boosters in 2015.
Bezos, however, has acknowledged the importance of reusing rocket parts since he founded the company in 2000 — two years before Musk established SpaceX. And the company has already developed its suborbital New Shepard tourism rocket to be reusable.
“It’s not a copy cat game,” Henry said. “Blue Origin has been pursuing reusable vehicles since before reusable vehicles were cool. Now it’s much more of a mainstream idea (because of SpaceX). The difference is that it’s taken Blue Origin so much longer to get to orbit.”
If successful, returning the New Glenn rocket booster for a safe landing will be a stunning feat. After expending most of its fuel to propel the rocket’s upper stage to space, the first-stage booster will need to make a clean separation. The booster must then maneuver with pinpoint guidance and reignite its engines with precision timing to avoid crashing into the ocean or the Jacklyn recovery platform.
What New Glenn will do
In some ways, New Glenn has already made its mark on the launch industry. Blue Origin has for years pitched the rocket to compete with both SpaceX and United Launch Alliance — a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin that buys engines from Blue Origin — for lucrative military launch contracts.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>omgomg</a>
The US Space Force selected Blue Origin, ULA and SpaceX in June to compete for $5.6 billion worth of Pentagon contracts for national security missions slated to launch over the next four years.
Blue Origin also has deals with several commercial companies to launch satellites. The contracts include plans to help deploy Amazon’s Kuiper internet satellites and a recently inked deal with AST SpaceMobile to help launch the Midland, Texas-based company’s space-based cellular broadband network.
New Glenn could also be instrumental in building Blue Origin’s planned space station, called Orbital Reef. Blue Origin and it commercial partners, including Sierra Space and Boeing, among others, hope the station will one day provide a new destination for astronauts as the International Space Station is phased out of service.
https://omgprice10.com
омг ссылка
New Glenn vs. other powerful rockets
New Glenn packs significant power. Dubbed a “heavy-lift” vehicle, its capabilities lie between SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and the more powerful Falcon Heavy launch vehicle.
SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9, for example, can haul up to 22.8 metric tons (50,265 pounds) to space. While New Glenn is capable of carrying about double that mass, it may also be roughly the same price as a Falcon 9: reportedly around $60 million to $70 million per launch.
“I think in order to compete with Falcon 9, you have to go head-to-head or better on price,” said Caleb Henry, the director of research at Quilty Space, which provides data and analysis about the space sector.
The question, however, is whether Blue Origin will be able to sustain a competitive price point, Henry added.
Still, one feature that makes New Glenn stand out is its large payload fairing, or nose cone. The component protects the cargo bay and is a whopping 23 feet (7 meters) wide — nearly 6 feet (2 meters) larger than that of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy.
Henry said Blue Origin likely opted to outfit New Glenn with such a large fairing in order to help fulfill Bezos’ vision of the future.
Most plane crashes are ‘survivable’
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken market</a>
First, the good news. “The vast majority of aircraft accidents are survivable, and the majority of people in accidents survive,” says Galea. Since 1988, aircraft — and the seats inside them — must be built to withstand an impact of up to 16G, or g-force up to 16 times the force of gravity. That means, he says, that in most incidents, “it’s possible to survive the trauma of the impact of the crash.”
For instance, he classes the initial Jeju Air incident as survivable — an assumed bird strike, engine loss and belly landing on the runway, without functioning landing gear. “Had it not smashed into the concrete reinforced obstacle at the end of the runway, it’s quite possible the majority, if not everyone, could have survived,” he says.
The Azerbaijan Airlines crash, on the other hand, he classes as a non-survivable accident, and calls it a “miracle” that anyone made it out alive.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken войти
Most aircraft involved in accidents, however, are not — as suspicion is growing over the Azerbaijan crash — shot out of the sky.
And with modern planes built to withstand impacts and slow the spread of fire, Galea puts the chances of surviving a “survivable” accident at at least 90%.
Instead, he says, what makes the difference between life and death in most modern accidents is how fast passengers can evacuate.
Aircraft today must show that they can be evacuated in 90 seconds in order to gain certification. But a theoretical evacuation — practiced with volunteers at the manufacturers’ premises — is very different from the reality of a panicked public onboard a jet that has just crash-landed.
Galea, an evacuation expert, has conducted research for the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) looking at the most “survivable” seats on a plane. His landmark research, conducted over several years in the early 2000s, looked at how passengers and crew behaved during a post-crash evacuation, rather than looking at the crashes themselves. By compiling data from 1,917 passengers and 155 crew involved in 105 accidents from 1977 to 1999, his team created a database of human behavior around plane crashes.
His analysis of which exits passengers actually used “shattered many myths about aircraft evacuation,” he says. “Prior to my study, it was believed that passengers tend to use their boarding exit because it was the most familiar, and that passengers tend to go forward. My analysis of the data demonstrated that none of these myths were supported by the evidence.”
The survivors of recent crashes were sitting at the back of the plane. What does that tell us about airplane safety?
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kra cc</a>
Look at the photos of the two fatal air crashes of the last two weeks, and amid the horror and the anguish, one thought might come to mind for frequent flyers.
The old frequent-flyer adage is that sitting at the back of the plane is a safer place to be than at the front — and the wreckage of both Azerbaijan Airlines flight 8243 and Jeju Air flight 2216 seem to bear that out.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken даркнет
The 29 survivors of the Azeri crash were all sitting at the back of the plane, which split into two, leaving the rear half largely intact. The sole survivors of the South Korean crash, meanwhile, were the two flight attendants in their jumpseats in the very tail of the plane.
So is that old adage — and the dark humor jokes about first and business class seats being good until there’s a problem with the plane — right after all?
In 2015, TIME Magazine reporters wrote that they had combed through the records of all US plane crashes with both fatalities and survivors from 1985 to 2000, and found in a meta-analysis that seats in the back third of the aircraft had a 32% fatality rate overall, compared with 38% in the front third and 39% in the middle third.
Even better, they found, were middle seats in that back third of the cabin, with a 28% fatality rate. The “worst” seats were aisles in the middle third of the aircraft, with a 44% fatality rate.
But does that still hold true in 2024?
According to aviation safety experts, it’s an old wives’ tale.
“There isn’t any data that shows a correlation of seating to survivability,” says Hassan Shahidi, president of the Flight Safety Foundation. “Every accident is different.”
“If we’re talking about a fatal crash, then there is almost no difference where one sits,” says Cheng-Lung Wu, associate professor at the School of Aviation of the University of New South Wales, Sydney.
Ed Galea, professor of fire safety engineering at London’s University of Greenwich, who has conducted landmark studies on plane crash evacuations, warns, “There is no magic safest seat.”
Scientists have identified an estimated 10% of all species on Earth. Here’s what they found in 2024
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken marketplace</a>
A toothy toadstool. A vegetarian piranha with a distinctive mark. And a pygmy pipehorse floating in the Indian Ocean shallows.
These wild wonders were among the hundreds of previously unknown species of animals, plants and fungi that scientists named and described for the first time in 2024, expanding our surprisingly limited knowledge of Earth’s diversity.
“Scientists estimate that we’ve identified only one-tenth of all species on Earth,” said Dr.
Shannon Bennett, chief of science at the California Academy of Sciences, in a statement.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken market
“While it is critical to place protections on known threatened species, we must also allocate resources towards identifying unknown species that may be just as important to the functioning of an ecosystem,” Bennett said.
Researchers connected to the institution described 138 new species in 2024, including 32 fish. One standout was a pygmy pipehorse named Cylix nkosi. The seahorse relative was originally found in 2021 in the cool temperate waters surrounding the North Island of New Zealand, but the species described this year was discovered in the subtropical waters off South Africa, expanding the known range of this group to the Indian Ocean
“South African reefs present notoriously difficult diving conditions with rough weather and intense, choppy waves — we knew we only had one dive to find it,” underwater photographer and marine biologist Richard Smith said in a statement.
“This species is also quite cryptic, about the size of a golf tee, but luckily we spotted a female camouflaged against some sponges about a mile offshore on the sandy ocean floor.”
The researchers involved in describing the new species chose nkosi as its name. A reference to the local Zulu word for “chief,” the name reflects the species’ crown-like head shape and acknowledges South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province where it was found.
New Glenn’s first flight
Blue Origin formally announced the development of New Glenn — which aims to outpower SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets and haul spacecraft up to 45 metric tons (99,200 pounds) to orbit — in 2016.
<a href=https://kra23att.cc>kraken darknet</a>
The vehicle is long overdue, as the company previously targeted 2020 for its first launch.
Delays, however, are common in the aerospace industry. And the debut flight of a new vehicle is almost always significantly behind schedule.
Rocket companies also typically take a conservative approach to the first liftoff, launching dummy payloads such as hunks of metal or, as was the case with SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy debut in 2018, an old cherry red sports car.
https://kra23att.cc
kraken marketplace
Blue Origin has also branded itself as a company that aims to take a slow, diligent approach to rocket development that doesn’t “cut any corners,” according to Bezos, who founded Blue Origin and funds the company.
The company’s mascot is a tortoise, paying homage to “The Tortoise and the Hare” fable that made the “slow and steady wins the race” mantra a childhood staple.
“We believe slow is smooth and smooth is fast,” Bezos said in 2016. Those comments could be seen as an attempt to position Blue Origin as the anti-SpaceX, which is known to embrace speed and trial-and-error over slow, meticulous development processes.
But SpaceX has certainly won the race to orbit. The company’s first orbital rocket, the Falcon 1, made a successful launch in September 2008. The company has deployed hundreds of missions to orbit since then.
And while SpaceX routinely destroys rockets during test flights as it begins developing a new rocket, the company has a solid track record for operational missions. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, for example, has experienced two in-flight failures and one launchpad explosion but no catastrophic events during human missions.
On a long-dormant pad in Florida, a rocket that could challenge SpaceX’s dominance is poised to launch
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>Площадка кракен</a>
On a Florida launchpad that has been dormant for almost two decades, a new, roughly 320-foot (98-meter) rocket — developed by Jeff Bezos’ company Blue Origin — is poised for its maiden flight.
The uncrewed launch vehicle, called New Glenn, will mark Blue Origin’s first attempt to send a rocket to orbit, a feat necessary if the company hopes to chip away at SpaceX’s long-held dominance in the industry.
New Glenn is set to lift off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station as early as next week.
https://kra23s.cc
kraken тор
The rocket, which stands about as tall as a 30-story building, consists of several parts: The first-stage rocket booster gives the initial thrust at liftoff. Atop the booster is an upper rocket stage that includes a cargo bay protected by a nose cone that will house experimental technology for this mission.
And, in an attempt to replicate the success that SpaceX has found reusing rocket boosters over the past decade, Blue Origin will also aim to guide New Glenn’s first-stage rocket booster back to a safe landing on a seafaring platform — named Jacklyn for Bezos’ mother — minutes after takeoff.
Like SpaceX, Blue Origin will seek to recover, refurbish and reuse first-stage rocket boosters to drive down costs.
For this inaugural mission, a smooth flight is not guaranteed.
But the eventual success of New Glenn, named after storied NASA astronaut John Glenn, is instrumental to some of Blue Origin’s most ambitious goals.
The rocket could one day power national security launches, haul Amazon internet satellites to space and even help in the construction of a space station that Blue Origin is developing with commercial partners.
Chile’s President Boric leads journey to South Pole in historic trip
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>kraken tor</a>
Chile’s President Gabriel Boric travelled to Antarctica’s South Pole on Friday, a place where no other Latin American president has set foot, according to the Chilean government.
Boric led the historic two-day trip, named Operation Pole Star III, to extend the environmental monitoring of pollutants on Antarctica, Chile’s government said in a statement.
He travelled with scientists, armed forces commanders and government ministers from the Chilean capital of Santiago to Punta Arenas, a city in southern Chile, public broadcaster Television Nacional de Chile (TVN) reported. From there, they made several stops before finally reaching the US-run Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, according to TVN.
https://kra23s.cc
kraken shop
Chile is one of seven countries that has a territorial claim in Antarctica, alongside Argentina, Australia, France, New Zealand, Norway and the United Kingdom.
It is also a signatory of the Antarctic Treaty, which dictates that the continent may only be used for peaceful and scientific purposes.
While Chile has historically carried out scientific activity in Antarctica’s northern sector, the country’s government is now hoping to expand research into the west of the continent, its statement said.
Boric called his trip to the South Pole an “honor” and a source of pride, TVN reported.
“This is a milestone for us. It is the first time a Chilean and Latin American President has visited the South Pole,” he said, according to TVN.
A year ago today, things went from bad to worse for Boeing
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken сайт</a>
At 5 p.m. PT on January 5, 2024, Boeing seemed like a company on the upswing. It didn’t last. Minutes later, a near-tragedy set off a full year of problems.
As Alaska Airlines flight 1282 climbed to 16,000 feet in its departure from Portland, Oregon, a door plug blew out near the rear of the plane, leaving a gaping hole in the fuselage. Phones and clothing were ripped away from passengers and sent hurtling into the night sky. Oxygen masks dropped, and the rush of air twisted seats next to the hole toward the opening.
https://kra23c.cc
Кракен даркнет
Fortunately, those were among the few empty seats on the flight, and the crew got the plane on the ground without any serious injuries. The incident could have been far worse — even a fatal crash.
Not much has gone right for Boeing ever since. The company has had one misstep after another, ranging from embarrassing to horrifying. And many of the problems are poised to extend into 2025 and perhaps beyond.
The problems were capped by another Boeing crash in South Korea that killed 179 people on December 29 in what was in the year’s worst aviation disaster. The cause of the crash of a 15-year old Boeing jet flown by Korean discount carrier Jeju Air is still under investigation, and it is quite possible that Boeing will not be found liable for anything that led to the tragedy.
But unlike the Jeju crash, most of the problems of the last 12 months have clearly been Boeing’s fault.
And 2024 was the sixth straight year of serious problems for the once proud, now embattled company, starting with the 20-month grounding of its best selling plane, the 737 Max, following two fatal crashes in late 2018 and early 2019, which killed 346 people.
Still the outlook for 2024 right before the Alaska Air incident had been somewhat promising. The company had just achieved the best sales month in its history in December 2023, capping its strongest sales year since 2018.
It was believed to be on the verge of getting Federal Aviation Administration approval for two new models, the 737 Max 7 and Max 10, with airline customers eager to take delivery. Approvals and deliveries of its next generation widebody, the 777X, were believed to be close behind. Its production rate had been climbing and there were hopes that it could be on the verge of returning to profitability for the first time since 2018.
What New Glenn will do
In some ways, New Glenn has already made its mark on the launch industry. Blue Origin has for years pitched the rocket to compete with both SpaceX and United Launch Alliance — a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin that buys engines from Blue Origin — for lucrative military launch contracts.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>omg ссылка на сайт</a>
The US Space Force selected Blue Origin, ULA and SpaceX in June to compete for $5.6 billion worth of Pentagon contracts for national security missions slated to launch over the next four years.
Blue Origin also has deals with several commercial companies to launch satellites. The contracts include plans to help deploy Amazon’s Kuiper internet satellites and a recently inked deal with AST SpaceMobile to help launch the Midland, Texas-based company’s space-based cellular broadband network.
New Glenn could also be instrumental in building Blue Origin’s planned space station, called Orbital Reef. Blue Origin and it commercial partners, including Sierra Space and Boeing, among others, hope the station will one day provide a new destination for astronauts as the International Space Station is phased out of service.
https://omgprice10.com
omgomg
New Glenn vs. other powerful rockets
New Glenn packs significant power. Dubbed a “heavy-lift” vehicle, its capabilities lie between SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and the more powerful Falcon Heavy launch vehicle.
SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9, for example, can haul up to 22.8 metric tons (50,265 pounds) to space. While New Glenn is capable of carrying about double that mass, it may also be roughly the same price as a Falcon 9: reportedly around $60 million to $70 million per launch.
“I think in order to compete with Falcon 9, you have to go head-to-head or better on price,” said Caleb Henry, the director of research at Quilty Space, which provides data and analysis about the space sector.
The question, however, is whether Blue Origin will be able to sustain a competitive price point, Henry added.
Still, one feature that makes New Glenn stand out is its large payload fairing, or nose cone. The component protects the cargo bay and is a whopping 23 feet (7 meters) wide — nearly 6 feet (2 meters) larger than that of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy.
Henry said Blue Origin likely opted to outfit New Glenn with such a large fairing in order to help fulfill Bezos’ vision of the future.
What’s on board this flight
Blue Origin had planned to launch a pair of Mars-bound satellites on behalf of NASA for the first flight of New Glenn.
But delays with the rocket’s development prompted the space agency to change course, moving that flight to this spring at the earliest. So for this inaugural flight, Blue Origin opted to instead fly a “demonstrator” that will test technology needed for the company’s proposed Blue Ring spacecraft — which will aim to serve as a sort of in-space rideshare vehicle, dragging satellites deeper into space when needed.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>omg omg onion</a>
The demonstrator on this New Glenn flight will remain aboard the rocket for the entire six-hour flight, Blue Origin said, and it will validate “communications capabilities from orbit to ground” as well as “test its in-space telemetry, tracking and command hardware, and ground-based radiometric tracking.”
The Blue Ring Pathfinder demonstrator is part of a deal Blue Origin inked with the US Department of Defense’s Defense Innovation Unit.
https://omgprice10.com
omg зайти
Why Blue Origin wants to reuse rockets
Similar to SpaceX, Blue Origin is aiming to recover and refly its first-stage rocket boosters in a bid to make launches less expensive.
“Reusability is integral to radically reducing cost-per-launch,” the company said in a recent news release, using the same oft-repeated sentiment that SpaceX has touted since it began landing rocket boosters in 2015.
Bezos, however, has acknowledged the importance of reusing rocket parts since he founded the company in 2000 — two years before Musk established SpaceX. And the company has already developed its suborbital New Shepard tourism rocket to be reusable.
“It’s not a copy cat game,” Henry said. “Blue Origin has been pursuing reusable vehicles since before reusable vehicles were cool. Now it’s much more of a mainstream idea (because of SpaceX). The difference is that it’s taken Blue Origin so much longer to get to orbit.”
If successful, returning the New Glenn rocket booster for a safe landing will be a stunning feat. After expending most of its fuel to propel the rocket’s upper stage to space, the first-stage booster will need to make a clean separation. The booster must then maneuver with pinpoint guidance and reignite its engines with precision timing to avoid crashing into the ocean or the Jacklyn recovery platform.
Chile’s President Boric leads journey to South Pole in historic trip
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>kraken войти</a>
Chile’s President Gabriel Boric travelled to Antarctica’s South Pole on Friday, a place where no other Latin American president has set foot, according to the Chilean government.
Boric led the historic two-day trip, named Operation Pole Star III, to extend the environmental monitoring of pollutants on Antarctica, Chile’s government said in a statement.
He travelled with scientists, armed forces commanders and government ministers from the Chilean capital of Santiago to Punta Arenas, a city in southern Chile, public broadcaster Television Nacional de Chile (TVN) reported. From there, they made several stops before finally reaching the US-run Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, according to TVN.
https://kra23s.cc
kraken зайти
Chile is one of seven countries that has a territorial claim in Antarctica, alongside Argentina, Australia, France, New Zealand, Norway and the United Kingdom.
It is also a signatory of the Antarctic Treaty, which dictates that the continent may only be used for peaceful and scientific purposes.
While Chile has historically carried out scientific activity in Antarctica’s northern sector, the country’s government is now hoping to expand research into the west of the continent, its statement said.
Boric called his trip to the South Pole an “honor” and a source of pride, TVN reported.
“This is a milestone for us. It is the first time a Chilean and Latin American President has visited the South Pole,” he said, according to TVN.
The survivors of recent crashes were sitting at the back of the plane. What does that tell us about airplane safety?
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>кракен вход</a>
Look at the photos of the two fatal air crashes of the last two weeks, and amid the horror and the anguish, one thought might come to mind for frequent flyers.
The old frequent-flyer adage is that sitting at the back of the plane is a safer place to be than at the front — and the wreckage of both Azerbaijan Airlines flight 8243 and Jeju Air flight 2216 seem to bear that out.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken сайт
The 29 survivors of the Azeri crash were all sitting at the back of the plane, which split into two, leaving the rear half largely intact. The sole survivors of the South Korean crash, meanwhile, were the two flight attendants in their jumpseats in the very tail of the plane.
So is that old adage — and the dark humor jokes about first and business class seats being good until there’s a problem with the plane — right after all?
In 2015, TIME Magazine reporters wrote that they had combed through the records of all US plane crashes with both fatalities and survivors from 1985 to 2000, and found in a meta-analysis that seats in the back third of the aircraft had a 32% fatality rate overall, compared with 38% in the front third and 39% in the middle third.
Even better, they found, were middle seats in that back third of the cabin, with a 28% fatality rate. The “worst” seats were aisles in the middle third of the aircraft, with a 44% fatality rate.
But does that still hold true in 2024?
According to aviation safety experts, it’s an old wives’ tale.
“There isn’t any data that shows a correlation of seating to survivability,” says Hassan Shahidi, president of the Flight Safety Foundation. “Every accident is different.”
“If we’re talking about a fatal crash, then there is almost no difference where one sits,” says Cheng-Lung Wu, associate professor at the School of Aviation of the University of New South Wales, Sydney.
Ed Galea, professor of fire safety engineering at London’s University of Greenwich, who has conducted landmark studies on plane crash evacuations, warns, “There is no magic safest seat.”
On a long-dormant pad in Florida, a rocket that could challenge SpaceX’s dominance is poised to launch
<a href=https://kra23s.cc>кракен ссылка</a>
On a Florida launchpad that has been dormant for almost two decades, a new, roughly 320-foot (98-meter) rocket — developed by Jeff Bezos’ company Blue Origin — is poised for its maiden flight.
The uncrewed launch vehicle, called New Glenn, will mark Blue Origin’s first attempt to send a rocket to orbit, a feat necessary if the company hopes to chip away at SpaceX’s long-held dominance in the industry.
New Glenn is set to lift off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station as early as next week.
https://kra23s.cc
кракен ссылка
The rocket, which stands about as tall as a 30-story building, consists of several parts: The first-stage rocket booster gives the initial thrust at liftoff. Atop the booster is an upper rocket stage that includes a cargo bay protected by a nose cone that will house experimental technology for this mission.
And, in an attempt to replicate the success that SpaceX has found reusing rocket boosters over the past decade, Blue Origin will also aim to guide New Glenn’s first-stage rocket booster back to a safe landing on a seafaring platform — named Jacklyn for Bezos’ mother — minutes after takeoff.
Like SpaceX, Blue Origin will seek to recover, refurbish and reuse first-stage rocket boosters to drive down costs.
For this inaugural mission, a smooth flight is not guaranteed.
But the eventual success of New Glenn, named after storied NASA astronaut John Glenn, is instrumental to some of Blue Origin’s most ambitious goals.
The rocket could one day power national security launches, haul Amazon internet satellites to space and even help in the construction of a space station that Blue Origin is developing with commercial partners.
Most plane crashes are ‘survivable’
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kraken сайт</a>
First, the good news. “The vast majority of aircraft accidents are survivable, and the majority of people in accidents survive,” says Galea. Since 1988, aircraft — and the seats inside them — must be built to withstand an impact of up to 16G, or g-force up to 16 times the force of gravity. That means, he says, that in most incidents, “it’s possible to survive the trauma of the impact of the crash.”
For instance, he classes the initial Jeju Air incident as survivable — an assumed bird strike, engine loss and belly landing on the runway, without functioning landing gear. “Had it not smashed into the concrete reinforced obstacle at the end of the runway, it’s quite possible the majority, if not everyone, could have survived,” he says.
The Azerbaijan Airlines crash, on the other hand, he classes as a non-survivable accident, and calls it a “miracle” that anyone made it out alive.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken даркнет
Most aircraft involved in accidents, however, are not — as suspicion is growing over the Azerbaijan crash — shot out of the sky.
And with modern planes built to withstand impacts and slow the spread of fire, Galea puts the chances of surviving a “survivable” accident at at least 90%.
Instead, he says, what makes the difference between life and death in most modern accidents is how fast passengers can evacuate.
Aircraft today must show that they can be evacuated in 90 seconds in order to gain certification. But a theoretical evacuation — practiced with volunteers at the manufacturers’ premises — is very different from the reality of a panicked public onboard a jet that has just crash-landed.
Galea, an evacuation expert, has conducted research for the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) looking at the most “survivable” seats on a plane. His landmark research, conducted over several years in the early 2000s, looked at how passengers and crew behaved during a post-crash evacuation, rather than looking at the crashes themselves. By compiling data from 1,917 passengers and 155 crew involved in 105 accidents from 1977 to 1999, his team created a database of human behavior around plane crashes.
His analysis of which exits passengers actually used “shattered many myths about aircraft evacuation,” he says. “Prior to my study, it was believed that passengers tend to use their boarding exit because it was the most familiar, and that passengers tend to go forward. My analysis of the data demonstrated that none of these myths were supported by the evidence.”
Scientists have identified an estimated 10% of all species on Earth. Here’s what they found in 2024
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>kra cc</a>
A toothy toadstool. A vegetarian piranha with a distinctive mark. And a pygmy pipehorse floating in the Indian Ocean shallows.
These wild wonders were among the hundreds of previously unknown species of animals, plants and fungi that scientists named and described for the first time in 2024, expanding our surprisingly limited knowledge of Earth’s diversity.
“Scientists estimate that we’ve identified only one-tenth of all species on Earth,” said Dr.
Shannon Bennett, chief of science at the California Academy of Sciences, in a statement.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken магазин
“While it is critical to place protections on known threatened species, we must also allocate resources towards identifying unknown species that may be just as important to the functioning of an ecosystem,” Bennett said.
Researchers connected to the institution described 138 new species in 2024, including 32 fish. One standout was a pygmy pipehorse named Cylix nkosi. The seahorse relative was originally found in 2021 in the cool temperate waters surrounding the North Island of New Zealand, but the species described this year was discovered in the subtropical waters off South Africa, expanding the known range of this group to the Indian Ocean
“South African reefs present notoriously difficult diving conditions with rough weather and intense, choppy waves — we knew we only had one dive to find it,” underwater photographer and marine biologist Richard Smith said in a statement.
“This species is also quite cryptic, about the size of a golf tee, but luckily we spotted a female camouflaged against some sponges about a mile offshore on the sandy ocean floor.”
The researchers involved in describing the new species chose nkosi as its name. A reference to the local Zulu word for “chief,” the name reflects the species’ crown-like head shape and acknowledges South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province where it was found.
A year ago today, things went from bad to worse for Boeing
<a href=https://kra23c.cc>Площадка кракен</a>
At 5 p.m. PT on January 5, 2024, Boeing seemed like a company on the upswing. It didn’t last. Minutes later, a near-tragedy set off a full year of problems.
As Alaska Airlines flight 1282 climbed to 16,000 feet in its departure from Portland, Oregon, a door plug blew out near the rear of the plane, leaving a gaping hole in the fuselage. Phones and clothing were ripped away from passengers and sent hurtling into the night sky. Oxygen masks dropped, and the rush of air twisted seats next to the hole toward the opening.
https://kra23c.cc
kraken войти
Fortunately, those were among the few empty seats on the flight, and the crew got the plane on the ground without any serious injuries. The incident could have been far worse — even a fatal crash.
Not much has gone right for Boeing ever since. The company has had one misstep after another, ranging from embarrassing to horrifying. And many of the problems are poised to extend into 2025 and perhaps beyond.
The problems were capped by another Boeing crash in South Korea that killed 179 people on December 29 in what was in the year’s worst aviation disaster. The cause of the crash of a 15-year old Boeing jet flown by Korean discount carrier Jeju Air is still under investigation, and it is quite possible that Boeing will not be found liable for anything that led to the tragedy.
But unlike the Jeju crash, most of the problems of the last 12 months have clearly been Boeing’s fault.
And 2024 was the sixth straight year of serious problems for the once proud, now embattled company, starting with the 20-month grounding of its best selling plane, the 737 Max, following two fatal crashes in late 2018 and early 2019, which killed 346 people.
Still the outlook for 2024 right before the Alaska Air incident had been somewhat promising. The company had just achieved the best sales month in its history in December 2023, capping its strongest sales year since 2018.
It was believed to be on the verge of getting Federal Aviation Administration approval for two new models, the 737 Max 7 and Max 10, with airline customers eager to take delivery. Approvals and deliveries of its next generation widebody, the 777X, were believed to be close behind. Its production rate had been climbing and there were hopes that it could be on the verge of returning to profitability for the first time since 2018.
New Glenn’s first flight
Blue Origin formally announced the development of New Glenn — which aims to outpower SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets and haul spacecraft up to 45 metric tons (99,200 pounds) to orbit — in 2016.
<a href=https://kra23att.cc>kraken сайт</a>
The vehicle is long overdue, as the company previously targeted 2020 for its first launch.
Delays, however, are common in the aerospace industry. And the debut flight of a new vehicle is almost always significantly behind schedule.
Rocket companies also typically take a conservative approach to the first liftoff, launching dummy payloads such as hunks of metal or, as was the case with SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy debut in 2018, an old cherry red sports car.
https://kra23att.cc
Кракен тор
Blue Origin has also branded itself as a company that aims to take a slow, diligent approach to rocket development that doesn’t “cut any corners,” according to Bezos, who founded Blue Origin and funds the company.
The company’s mascot is a tortoise, paying homage to “The Tortoise and the Hare” fable that made the “slow and steady wins the race” mantra a childhood staple.
“We believe slow is smooth and smooth is fast,” Bezos said in 2016. Those comments could be seen as an attempt to position Blue Origin as the anti-SpaceX, which is known to embrace speed and trial-and-error over slow, meticulous development processes.
But SpaceX has certainly won the race to orbit. The company’s first orbital rocket, the Falcon 1, made a successful launch in September 2008. The company has deployed hundreds of missions to orbit since then.
And while SpaceX routinely destroys rockets during test flights as it begins developing a new rocket, the company has a solid track record for operational missions. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, for example, has experienced two in-flight failures and one launchpad explosion but no catastrophic events during human missions.
What’s on board this flight
Blue Origin had planned to launch a pair of Mars-bound satellites on behalf of NASA for the first flight of New Glenn.
But delays with the rocket’s development prompted the space agency to change course, moving that flight to this spring at the earliest. So for this inaugural flight, Blue Origin opted to instead fly a “demonstrator” that will test technology needed for the company’s proposed Blue Ring spacecraft — which will aim to serve as a sort of in-space rideshare vehicle, dragging satellites deeper into space when needed.
<a href=https://omgprice10.com>омг ссылка</a>
The demonstrator on this New Glenn flight will remain aboard the rocket for the entire six-hour flight, Blue Origin said, and it will validate “communications capabilities from orbit to ground” as well as “test its in-space telemetry, tracking and command hardware, and ground-based radiometric tracking.”
The Blue Ring Pathfinder demonstrator is part of a deal Blue Origin inked with the US Department of Defense’s Defense Innovation Unit.
https://omgprice10.com
omgprice10 cc
Why Blue Origin wants to reuse rockets
Similar to SpaceX, Blue Origin is aiming to recover and refly its first-stage rocket boosters in a bid to make launches less expensive.
“Reusability is integral to radically reducing cost-per-launch,” the company said in a recent news release, using the same oft-repeated sentiment that SpaceX has touted since it began landing rocket boosters in 2015.
Bezos, however, has acknowledged the importance of reusing rocket parts since he founded the company in 2000 — two years before Musk established SpaceX. And the company has already developed its suborbital New Shepard tourism rocket to be reusable.
“It’s not a copy cat game,” Henry said. “Blue Origin has been pursuing reusable vehicles since before reusable vehicles were cool. Now it’s much more of a mainstream idea (because of SpaceX). The difference is that it’s taken Blue Origin so much longer to get to orbit.”
If successful, returning the New Glenn rocket booster for a safe landing will be a stunning feat. After expending most of its fuel to propel the rocket’s upper stage to space, the first-stage booster will need to make a clean separation. The booster must then maneuver with pinpoint guidance and reignite its engines with precision timing to avoid crashing into the ocean or the Jacklyn recovery platform.